Elements—a kind of pure substance
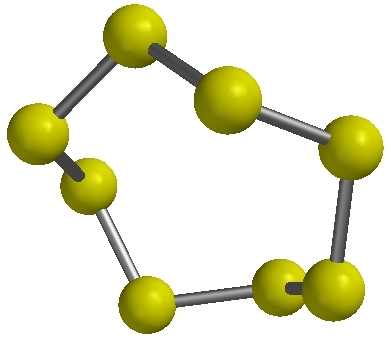
A single molecule
of sulfur (S8)
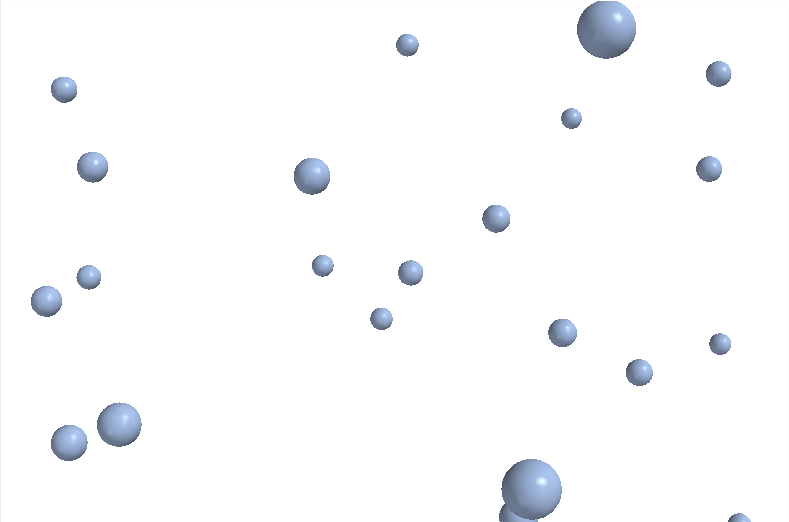
Argon (Ar) gas
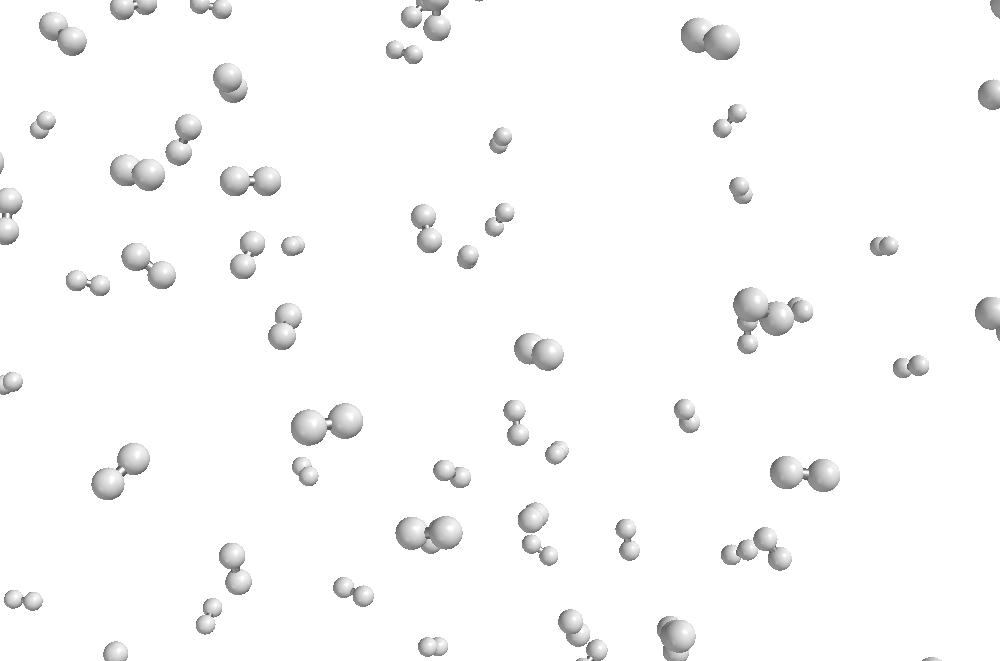

Hydrogen (H2) gas
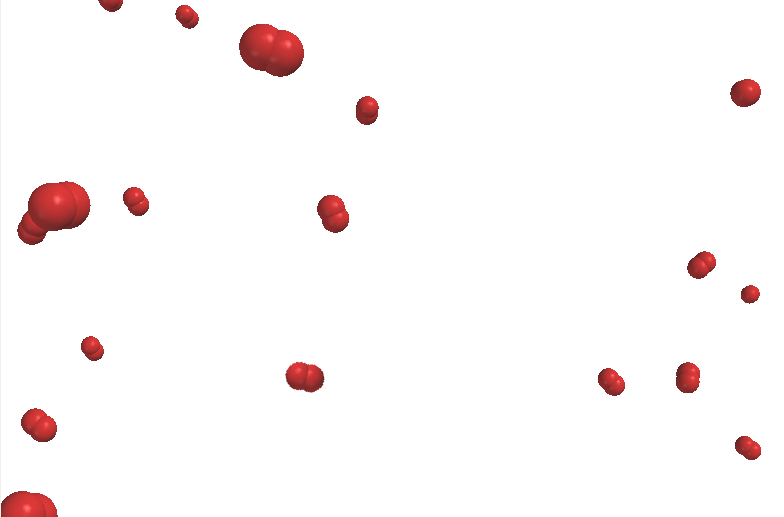

Oxygen (O2) gas
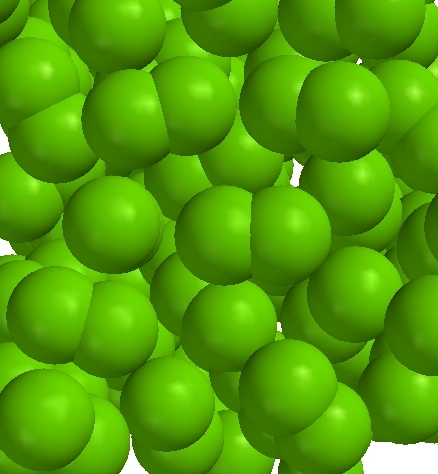
Liquid chlorine (Cl2)
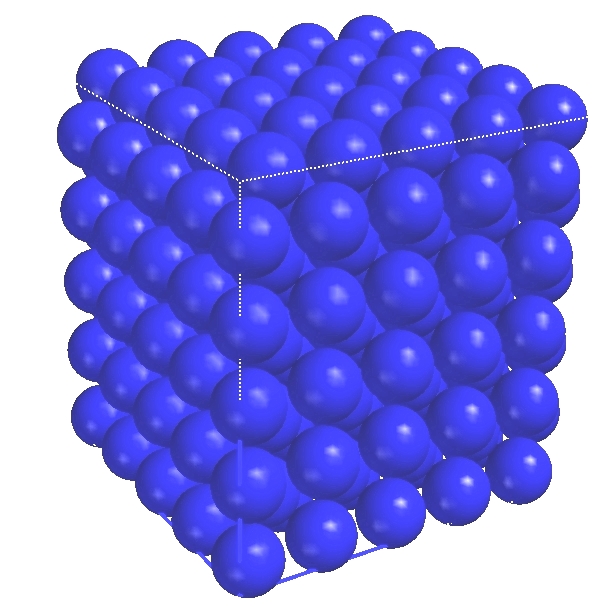
Solid sodium (Na)
Matter is made of particles. Particles may be single atoms or they may be molecules. Molecules are groups of atoms bound together by chemical bonds. Pure substances are materials made up of only one kind of particle. One type of pure substance is an element. Elements are substances made from only one kind of atom. Another type of pure substance is a compound. Compounds are made from two or more kinds of atoms bound by chemical bonds in a specific ratio.
If the smallest atom, hydrogen (H), is a golf ball then the largest atom, rubidium (Rb) is a basketball. The atoms in these pictures are not on the same scale as one another so size differences should not be taken literally.
Elements—a kind of pure substance | ||
 A single molecule of sulfur (S8) |
 Argon (Ar) gas |
 Hydrogen (H2) gas |
 Oxygen (O2) gas |
 Liquid chlorine (Cl2) |
 Solid sodium (Na) |
A material is made of many particles. One atom or one molecule is not enough. Elements may be made up of particles that are single atoms (monatomic elements) or they may be made up of particles that are molecules. Molecules of elements have two or more atoms of the same type bound together by chemical bonds. Here is a list of elements which exist as molecules: hydrogen (H2), nitrogen (N2), oxygen (O2), ozone (O3), fluorine (F2), chlorine (Cl2), bromine (Br2), iodine (I2), phosphorus (P4), and sulfur (S8).
Compounds—a kind of pure substance | ||
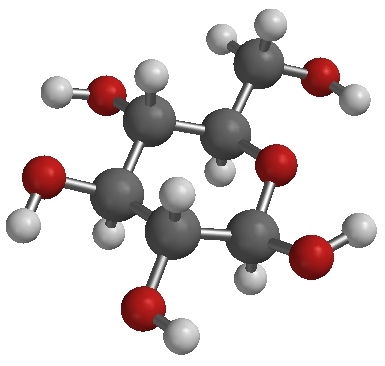 A single molecule of glucose (C6H12O6) |
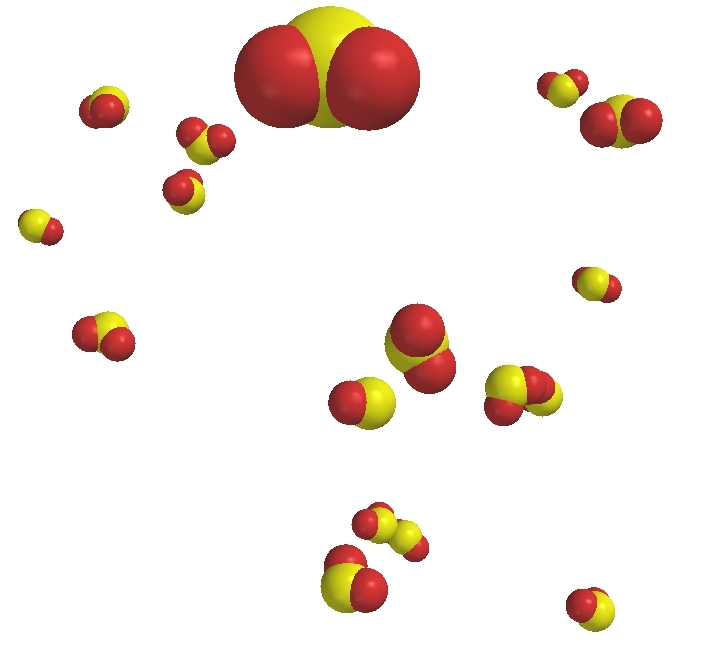
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) gas |
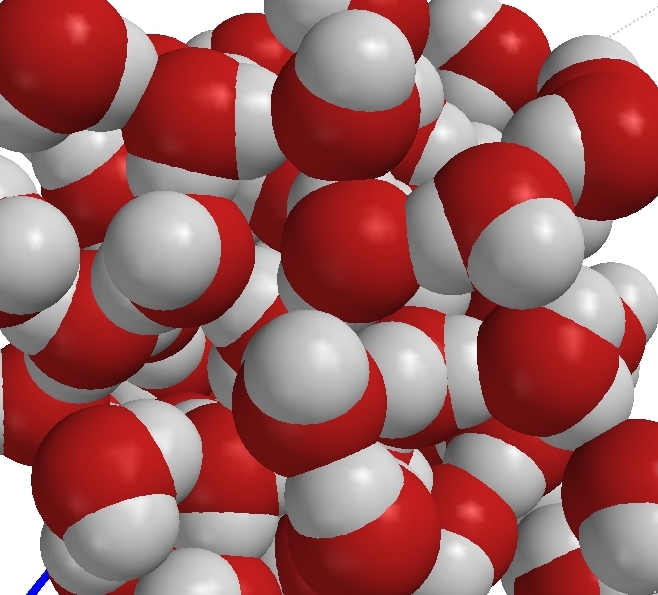
Liquid water (H2O) |
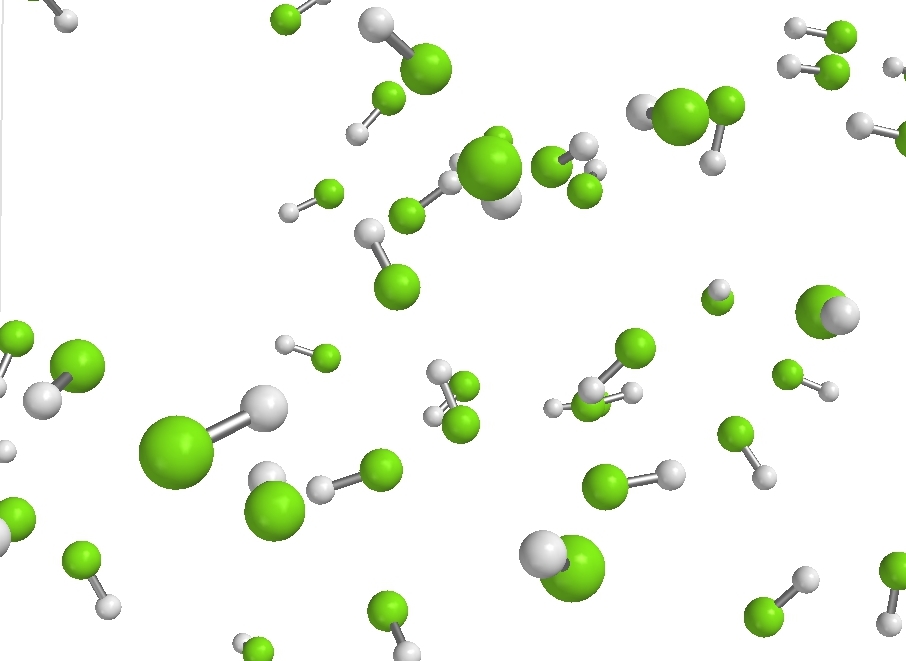
Hydrogen chloride (HCl) gas |
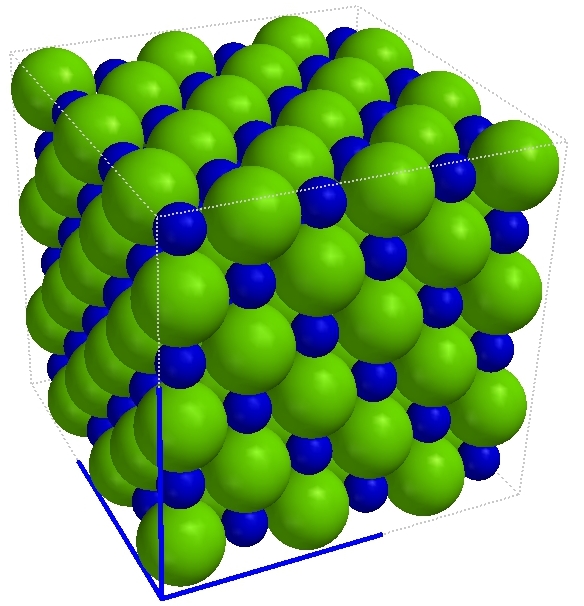 Solid sodium chloride (NaCl) |
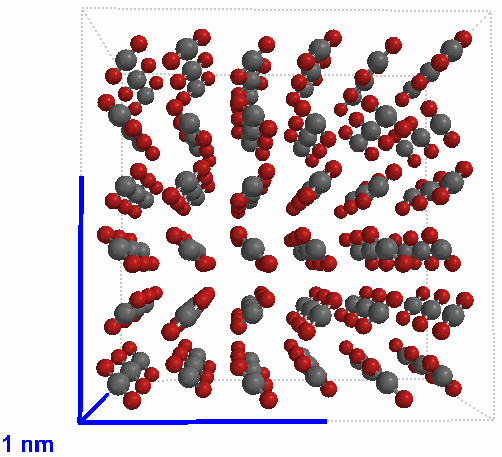
Solid carbon dioxide (CO2) |
Compounds are pure substances made of atoms of two or more elements bound by chemical bonds in a specific ratio. Though there are different kinds of atoms in compounds, they are not mixtures because the different kinds of atoms cannot be physically separated. Note that oxygen atoms are found in four of the compounds depicted on this page. Those atoms remain of the oxygen-type but are not the same as the element oxygen. The element oxygen is a gas made of particles which are molecules made of two atoms of the oxygen type. In order to get oxygen out of the water, for example, a chemical reaction must occur.
Mixtures are all characterized by the fact that there in a mixture there are always two or more types of particles. Homogeneous mixtures are those in which the particles of all substances do not form clumps, bubbles, or layers. All of the molecules touch all of the other molecules. In a heterogeneous mixture the particles of one substance may form clumps. Inside these clumps particles of that substance only touch others of the same kind. Bubbles and droplets of liquids are good examples. Sometimes certain substances will not mix with one another at all. Such substances may form layers. The less dense material always floats on top.
Mixtures may have variable proportions of the substances that make them up. Salt water may be anywhere from 1% to 26% salt by mass, for example.
Finally, mixtures can be physically separated into the individual pure substances that make them up. Sand can be filtered out of water. Water can be boiled and the steam collected to separate water from things like dissolved salt or sugar. Small pieces of iron can be separated from mixtures with other materials by using magnets. If the materials mixed together are large enough it may even be possible to simply sort out different materials by hand.
Some examples of homogeneous mixtures:
Some examples of heterogeneous mixtures:
Homogeneous Mixtures | ||
.jpg) Sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolved in water (H2O) |
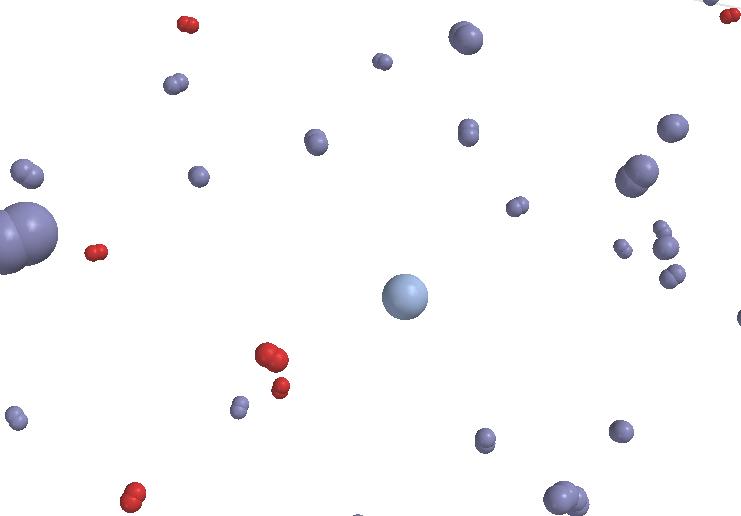
Air: a mixture of 78% nitrogen (N2), 21% oxygen (O2), and 1% argon (Ar) |
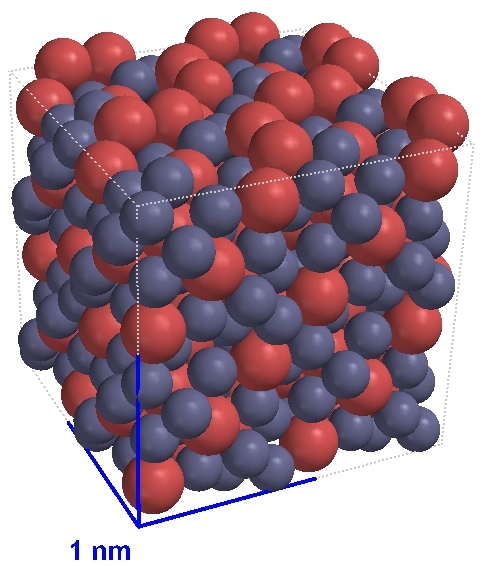 Brass: a solid mixture of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn) In this sample there are five copper atoms for every 8 zinc atoms but this ratio can be varied. |
Heterogeneous Mixtures | ||
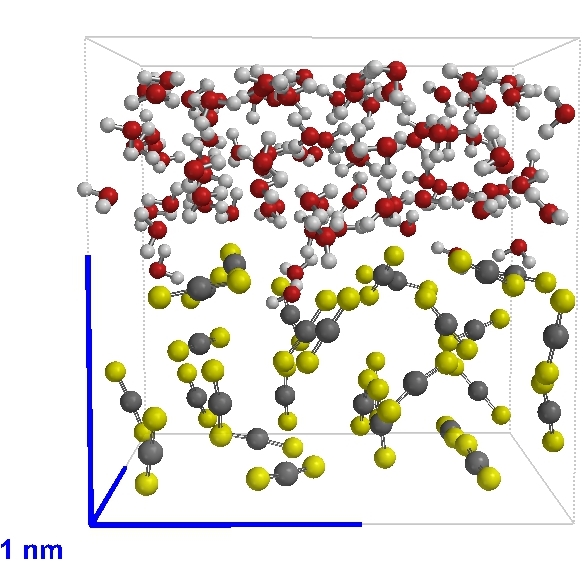 Carbon disulfide (CS2) in a layer under water (H2O) |
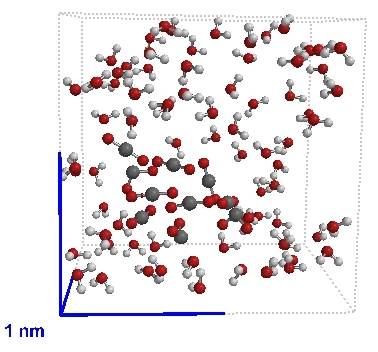 A bubble of carbon dioxide (CO2) in water (H2O) |

Sand is a complex mixture of different minerals (This is not a molecular-level image) |