This lab is a computer-simulation-based activity. The original simulation requires Java and may not run on all computers. The creators of the PhET site have arranged for an emulated version to run in a browser on most devices. If it won’t run on student machines the activity can be done by showing the simulator using a computer-projection system. The simulator is available for download at https://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulations/sugar-and-salt-solutions. Or, perhaps more easily accessed by performing a search for “PhET Sugar and Salt”.
 |
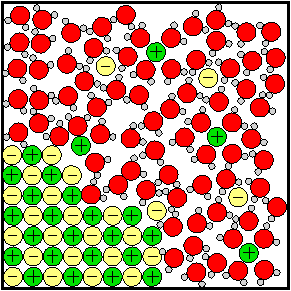
| Salt dissolving in water. The salt ions are positive and negative. The water molecules have one large oxygen atom and two small hydrogen atoms. |
 |
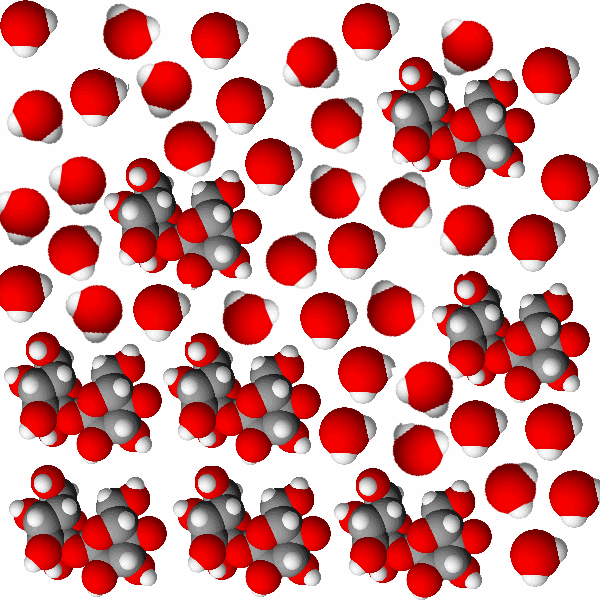
| Sugar dissolving in water. The sugar molecules are the large groups of atoms. The molecules in the solid are stuck together but the dissolved sugar molecules move separately while remaining whole sugar molecules. |
Sugar and salt both dissolve easily in water and they look a lot alike. There is an important difference between them, though. Salt is an ionic compound made up of two kinds of ion: sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl–). Sugar is a molecular compound made of one kind of molecule: C12H22O11.
Though it looks the same to the naked eye when you add a spoonful of either of these substances to water, what happens to the ions or molecules is quite different. The ions of the salt separate and become surrounded by water molecules. The chemical formula of salt is broken in half and instead of having just one kind of thing dissolved in the water there are two, a positive ion and a negative ion. See the image at right.
When sugar dissolves the molecules separate from each other but the chemical formula stays together. There is just one kind of thing dissolved in the water and it is neutrally charged. See the image at right.
Ionic compounds are also called electrolytes. An electrolyte is a material which breaks up into ions when it dissolves in water. When electrolytes dissolve in water they cause the water to be able to conduct electricity. Molecular compounds are usually non-electrolytes. A non-electrolyte is a material that dissolves in water as whole molecules: no ions are produced and the water does not gain the ability to conduct electricity.
Put the conductivity tester into the water in the simulator on the “Macro” tab.
Switch to the “Micro” tab. Remember that you already know how to classify elements as metals or non-metals. This is important for this part of the activity. Remember, too, that molecular compounds are composed of non-metal elements and that ionic compounds are composed of ions, usually a metal ion and a non-metal ion.