| molybdenum-96 Z = 42 & A = 96 Z = the number of protons Z = the atomic number A = the atomic mass A = the atomic mass number Z + n0 = A or A - Z = n0 |
|
| molybdenum-96 Z = 42 & A = 96 Z = the number of protons Z = the atomic number A = the atomic mass A = the atomic mass number Z + n0 = A or A - Z = n0 |
|
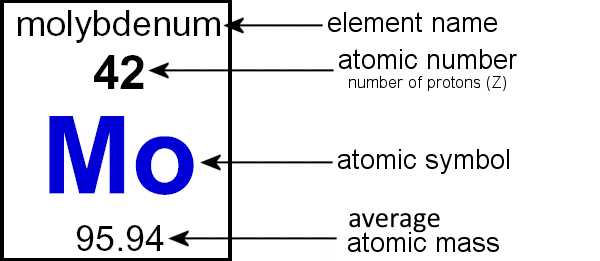
Fill in the table showing Z and A in the symbol, like in the example of molybdenum given above. Since these atoms are neutral they have the same number of electrons as protons. So the overall charge for all of them is 0.
For these problems you need to know how to read the names of
isotopes.
In aluminum-27 the word gives you the name of
the element. The number gives you the mass of the isotope. Find
the element on the periodic table. The atomic number (see key
above) tells you how many protons that element has. The mass
tells you the sum of protons plus neutrons for that isotope.
| Name | Symbol | Z No. of p+ |
A - Z No. of n0 |
A Mass |
No. of e– | Overall Charge |
| nitrogen-15 | 157N | 7 | 8 | 15 | 7 | 0 |
| ___92 ___ | 235 | 0 | ||||
| 39 | 18 | 0 | ||||
| nickel-64 | 0 | |||||
| 59 | 28 | 0 | ||||
| 28 | 56 | 0 | ||||
| 22 | 41 | 0 | ||||
| 82___Kr | 0 | |||||
| 100___Mo | 0 | |||||
| tin-120 | 0 | |||||
| ___50 ___ | 65 | 0 | ||||
| ___19 ___ | 39 | 0 | ||||
| 14______ | 7 | 0 |
You will color your Periodic Table according to a color scheme shown by your teacher. The periodic table is divided up into groups and periods. The groups are columns and are numbered from 1 to 18. The power of the periodic table comes from the fact that elements in each group all have similar properties. Take the Noble Gases, group 18. All of these elements share the common trait that they have practically no chemical reactivity at all. That means that they do not combine with other atoms to form compounds. The periods are the rows of the periodic table. The rows below the main table that start with lanthanum ( La) and actinium (Ac) belong to periods six and seven.
The color scheme you will use is a bit complicated. This is because the block on the right side consists of metals, semi-metals, and non-metals. Metals are shiny, conduct electricity and heat well, and are easily bent and shaped. Non-metals are dull-colored, do not conduct electricity or heat, and are brittle (or are gases). Semi-metals have traits of both metals and non-metals.
Use your notes and the information on this worksheet to answer the following questions. Answer using complete sentences.