You have learned about atomic structure. You know that the atomic nucleus is positively charged and it is orbited by negatively charged electrons. When atoms gain electrons they are a type of ion called an anion (AN-eye-on). Anions have a negative charge. When atoms lose electrons they are a type of ion called a cation (CAT-eye-on). Cations have a positive charge.
| Before | After | ||||||
| 1 | Na | + | energy |
|
Na+1 | + | e– |
| 2 | Cl | + | e– |
|
Cl–1 | + | energy |
| 3 | Fe | + | energy |
|
Fe+1 | + | e– |
| 4 | I | + | e– |
|
I–1 | + | energy |
|
Name & Symbol of Element |
Charge before |
Number of Protons |
Number of Electrons before |
Charge after |
Cation or Anion? |
Number of Electrons after |
|
| 1 | |||||||
| 2 | |||||||
| 3 | |||||||
| 4 |
When an atom loses an electron it must absorb some energy in order to pull the negative electron away from the positive nucleus because opposite charges attract. Ionization is the name for the process when an atom absorbs some energy and loses an electron as a result.
Radiation is the emission of energy or particles that move outward along rays. There are two basic types of radiation. The first type of radiation is harmless to living things unless it is extremely intense. This type is generally known as non-ionizing radiation. The second can cause ionization and is called ionizing radiation. Ionization is when an atom or molecule loses an electron and becomes positively charged.
Light is a form of radiation. Radio waves, microwaves, infrared light, visible light, ultraviolet light, x-rays and gamma rays are just different names for the same thing: electromagnetic radiation. These different names reflect differences in energy. The microwaves used to heat your food in a microwave oven are the same as the microwaves used to transmit your cell-phone calls. Microwave radiation is a form of low-energy electromagnetic radiation. Radio waves, microwaves, infrared light and visible light are all too low in energy to cause any damage to living things. These are the only types of non-ionizing radiation.
| Non-ionizing Radiation | |||||
| Type | Type of Particle | Mass | Speed | Picture | Facts |
| Radio Waves | Photon | 0 amu | 3 × 108 m/s |
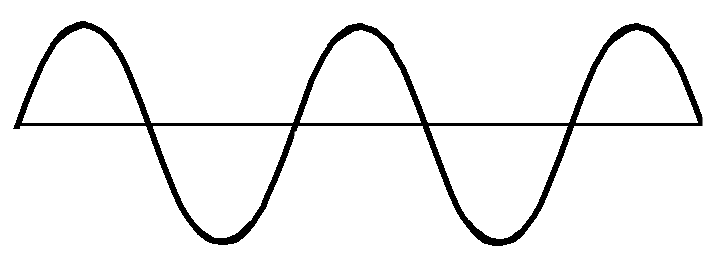
|
Many types of matter are transparent to radio waves. Used for communication. |
| Microwaves | Photon | 0 amu | 3 × 108 m/s |

|
Passes through most materials but can cause warming in others. Used for communication and cell phones and cooking. |
| Infrared Light | Photon | 0 amu | 3 × 108 m/s |
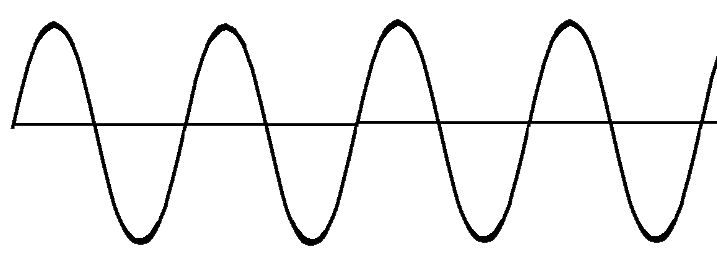
|
Also called ‘heat radiation’ because all objects with a temperature radiate light in the infrared. Used in remote controls and for night vision. |
| Visible Light | Photon | 0 amu | 3 × 108 m/s |

|
A narrow range of wavelengths which can be perceived by the human eye. This type of light can excite electrons in atoms and molecules. |
Answer the following questions using Model 2.
Of the types of electromagnetic radiation, only ultraviolet rays, x-rays and gamma rays can directly cause atoms or molecules to become ionized. Ultraviolet rays can cause sun burns and exposure over time can lead to the development of cancer. They do this by breaking chemical bonds between atoms in molecules. X-rays and gamma rays mostly pass right through living things but if they hit an atom or molecule they can also break chemical bonds and knock electrons loose.
There are two other forms of radiation that can cause ionization and they are fundamentally different from electro-magnetic radiation (or light). Light can be understood to be made of little packets of pure energy called photons, which have no mass. Alpha particles are massive particles with a +2 positive charge. An alpha particle is a high-speed helium-4 (42He) nucleus which is ejected by the nucleus of a large, unstable atomic nucleus. Because of its positive charge and large mass and incredible speed an alpha particle (also written α-particle) can cause a large number of atoms to become ionized.
Beta-rays (also written β-rays) are high-speed electrons ejected by an unstable atomic nucleus. They come from a neutron in the nucleus which is transformed into a proton. In the process the electron flies out of the nucleus. Even though it has a small mass a β-particle is strongly ionizing because of its very large speed and because of its –1 electric charge.
| Ionizing Radiation | |||||
| Type | Type of Particle | Mass | Speed | Picture | Facts |
| Ultraviolet | Photon | 0 amu | 3 × 108 m/s |
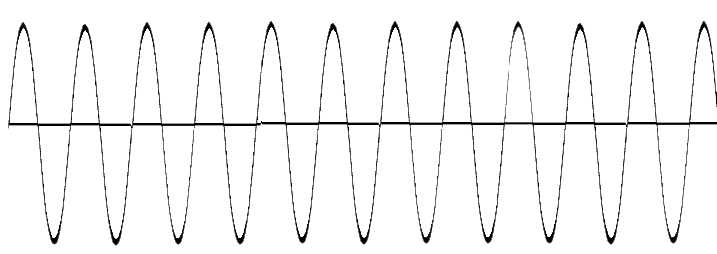
|
Single photons are capable of breaking chemical bonds and separating electrons from atoms, also known as ionization. |
| X-rays | Photon | 0 amu | 3 × 108 m/s |

|
Passes through most materials but can cause damage if it does not. When a photon strikes an atom or molecule it is likely to cause ionization. |
|
Gamma Rays (γ-rays) |
Photon | 0 amu | 3 × 108 m/s |

|
Passes through most materials but can cause damage if it does not. When a photon strikes an atom or molecule it is likely to cause ionization. Gamma ray photons originate in the nucleus of an atom. |
|
Alpha Rays (α-rays) |
Alpha Particle | 4 amu | 1.5 × 107 m/s |
|
An alpha-particle is a high-speed helium-4 nucleus (+2 charge) ejected by an unstable atomic nucleus. Very strongly ionizing. |
|
Beta Rays (β-rays) |
Beta Particle | 5.49 × 10–4 amu | 3 × 107 m/s | e– | A beta-particle is a high-speed electron (–1 charge) ejected by an unstable atomic nucleus. Very strongly ionizing. |
Answer the following questions using Model 3.